Learn about various types of Industrial Robots and their applications
Did you know that Industrial Robots have revolutionized the manufacturing industry? These machines are designed to perform repetitive tasks with precision, speed, and accuracy, making them an essential part of modern factories. In this video, we will explore the different types of Industrial Robots and their applications.
Industrial Robots come in various shapes and sizes, each serving a specific purpose. Let's dive into some of the most common types:
1. Articulated Robots: These robots have rotary joints, similar to a human arm. They can perform tasks with a high degree of freedom and are widely used in assembly lines, welding, and material handling.
2. SCARA Robots: SCARA stands for Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm. These robots have two parallel rotary joints and can move in a horizontal plane. They excel in tasks that require fast and precise movements, such as pick-and-place operations in electronics manufacturing.
3. Cartesian Robots: Also known as Gantry Robots, Cartesian Robots have three linear axes that can move independently. They are often used in applications that require heavy lifting, such as loading and unloading materials in warehouses.
4. Delta Robots: Delta Robots have a unique structure with three arms connected to a central base. They are known for their incredible speed and precision, making them ideal for tasks that involve high-speed pick-and-place operations, such as packaging and sorting.
5. Collaborative Robots: Collaborative Robots, also known as cobots, are designed to work alongside humans. They are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features that allow them to safely interact with humans without the need for protective barriers. Cobots are becoming increasingly popular in industries like healthcare, where they assist with tasks like patient care and medication dispensing.
Now that we have explored the different types of Industrial Robots, let's take a look at their applications:
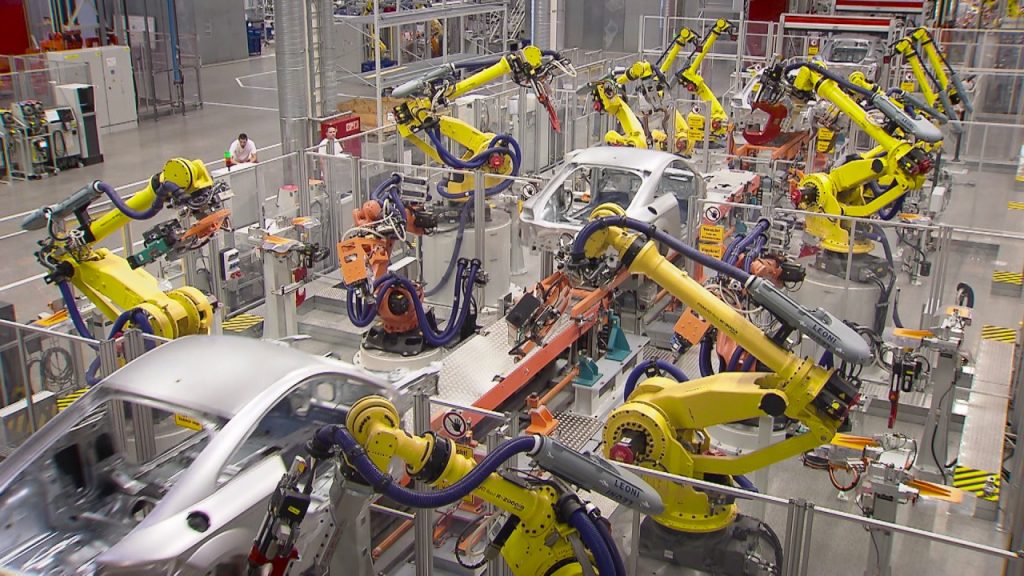
1. Assembly: Industrial Robots are widely used in assembly lines, where they can quickly and accurately assemble products. They can handle intricate tasks that require precision, such as inserting small components or fastening screws.
2. Welding: Robots are commonly used for welding applications, as they can perform repetitive welding tasks with consistent quality. They can work in challenging environments and handle complex welding patterns.
3. Material Handling: Industrial Robots excel at material handling tasks, such as loading and unloading heavy objects. They can lift and move items with precision, reducing the risk of injuries and increasing efficiency.
4. Packaging: Robots play a crucial role in packaging operations. They can quickly package products into boxes, apply labels, and even stack them on pallets. This automation improves productivity and ensures consistency in packaging quality.
5. Inspection and Quality Control: Industrial Robots equipped with vision systems can perform inspections and quality control checks. They can detect defects, measure dimensions, and ensure that products meet the required standards.
Industrial Robots have transformed the manufacturing industry, improving efficiency, productivity, and safety. They have become an integral part of the Industry 4.0 revolution, where automation and digitalization are driving significant advancements.
In conclusion, Industrial Robots come in various types, each with its own set of applications. From assembly and welding to material handling and packaging, these robots have revolutionized the way goods are manufactured. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of Industrial Robots in the future.
Check the coil packing solution with a leading manufacturer for the professional solution just here: [insert relevant CTA] Industrial Robot
"Demystifying Industrial Robots: A Comprehensive Overview of Types and Applications"