Check out our website to learn more about our professional coil packing solutions."
Title: Mastering Industrial Robot Programming: A Step-by-Step Guide to Welding Robot Programming
Introduction:
Welcome to our YouTube video tutorial on the basics of programming a welding robot for both linear and circular welds using Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW). In this video, we will walk you through the fundamentals of industrial robot programming and provide you with a comprehensive guide to successfully program a welding robot.
Industrial Robot Programming: An Overview:
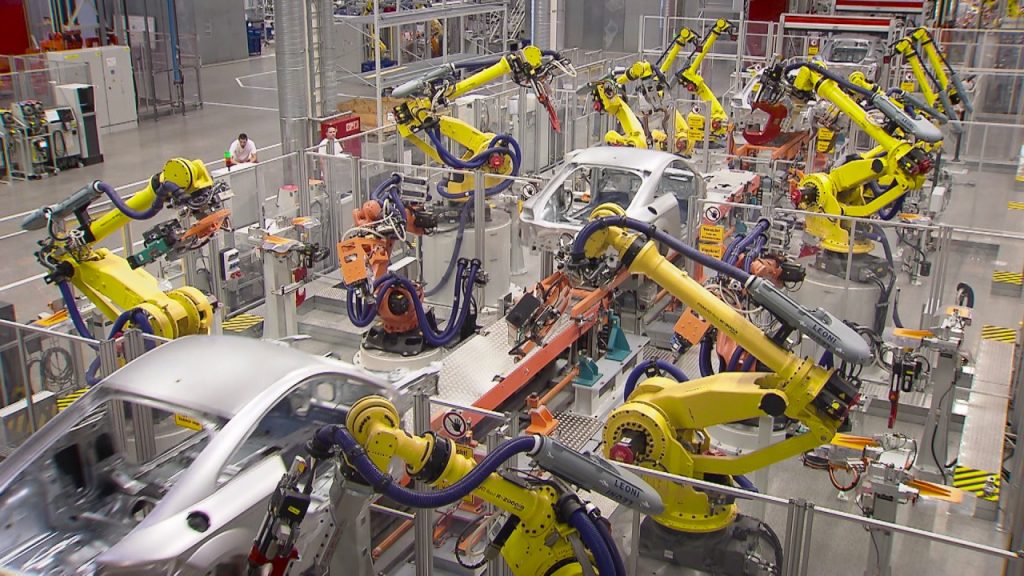
Industrial robot programming involves the creation of instructions or commands that enable robots to perform specific tasks autonomously. With the advancements in technology, robots have become an integral part of various industries, including manufacturing. The ability to program robots to perform welding tasks has revolutionized the welding industry, making it more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective.
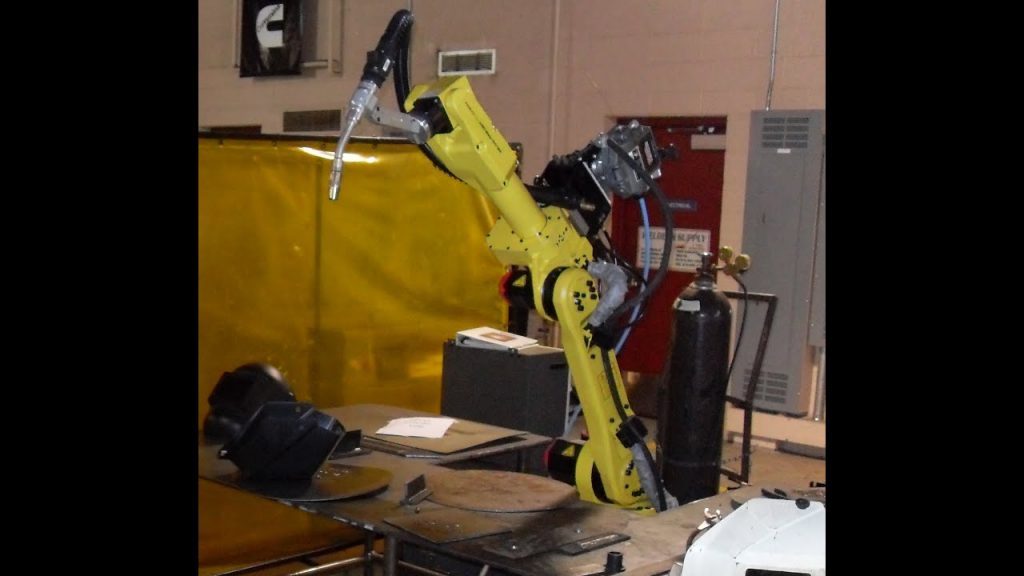
Understanding Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW):
GMAW, also known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, is a widely used welding process that utilizes a consumable electrode wire and a shielding gas to create an electric arc between the electrode and the workpiece. This process is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication.
Programming Basics: Linear and Circular Welds:
1. Linear Welds:
Programming a welding robot for linear welds involves defining the start and end points of the weld path, as well as the desired speed and welding parameters. By accurately programming the robot, you can ensure consistent and precise welds along a straight line.
2. Circular Welds:
Circular welds require additional programming techniques to specify the center point, radius, and angle of the weld path. With the right programming, the welding robot can effortlessly perform circular welds with high precision.
Step-by-Step Guide to Programming a Welding Robot:
1. Preparation:
- Ensure that the welding robot is properly calibrated and set up for the welding task.
- Gather all necessary data, such as the dimensions of the workpiece and the desired welding parameters.
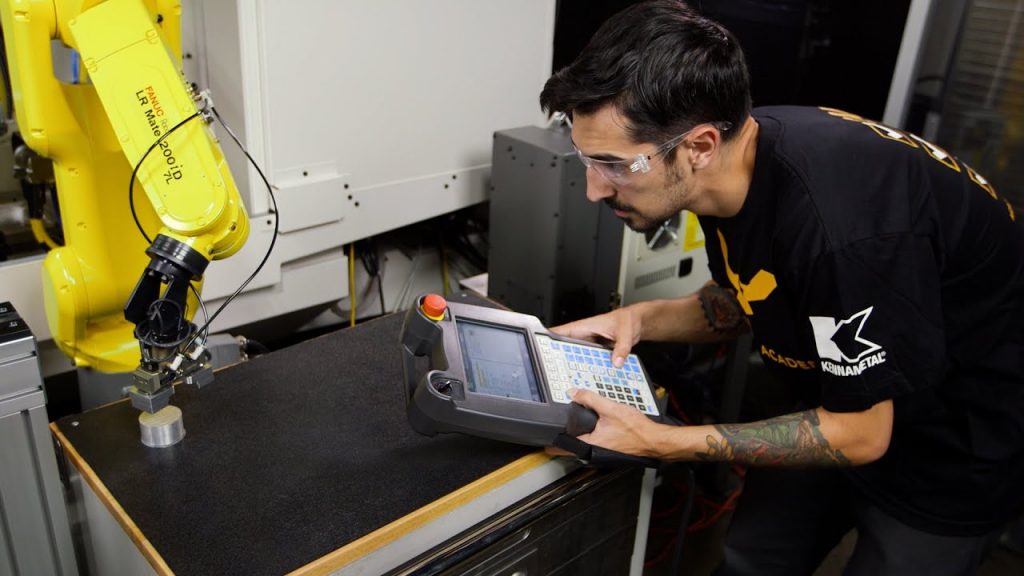
2. Robot Control Software:
- Familiarize yourself with the robot control software, which allows you to program the robot's movements and welding parameters.
- Create a new program and define the welding path using the software's intuitive interface.
3. Programming Linear Welds:
- Specify the start and end points of the weld path using the software's coordinate system.
- Adjust the speed and welding parameters to achieve the desired weld quality.
- Test and fine-tune the program to ensure optimal performance.
4. Programming Circular Welds:
- Define the center point, radius, and angle of the circular weld using the software's dedicated features.
- Verify the welding path visually and make any necessary adjustments.
- Run test welds to validate the program's accuracy and adjust as needed.
Conclusion:
Mastering industrial robot programming is essential for maximizing the capabilities of welding robots. By following the step-by-step guide provided in this video, you can confidently program a welding robot to perform both linear and circular welds using the Gas Metal Arc Welding process. Embrace the power of automation and enhance your welding operations with the precision and efficiency of industrial robot programming.
Remember, for professional coil packing solutions, check out our website to learn more about our offerings and how they can benefit your specific needs. Industrial Robot
"Mastering Welding Robot Programming: Essential Techniques for Industrial Automation"