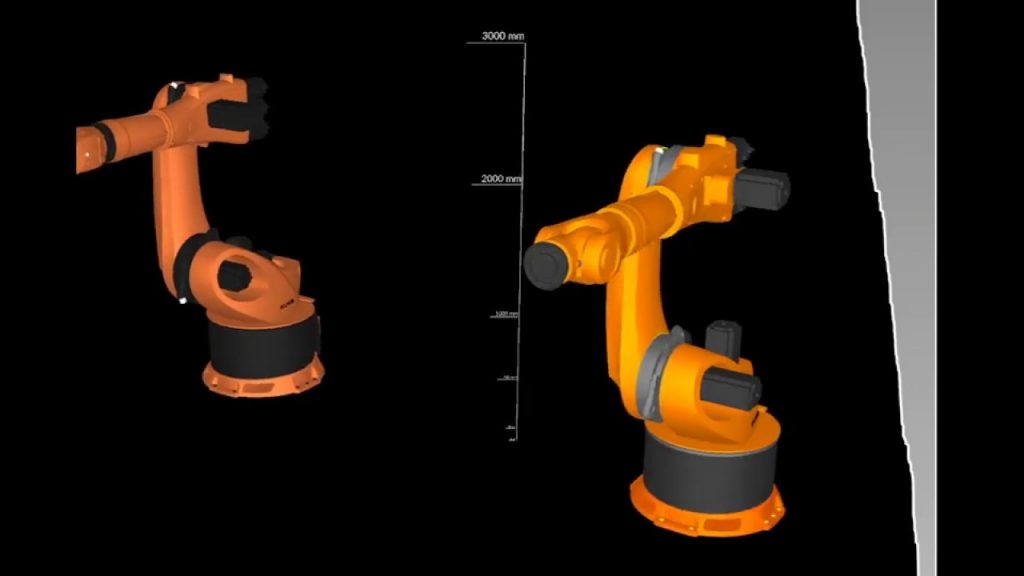
If you're interested in learning about the different types of industrial robots, then you're in the right place. In this article, we will be discussing the various types of industrial robots, ranging from the smallest and most compact robot arms to the largest ones capable of lifting heavy loads. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the different types of industrial robots available in the market today.
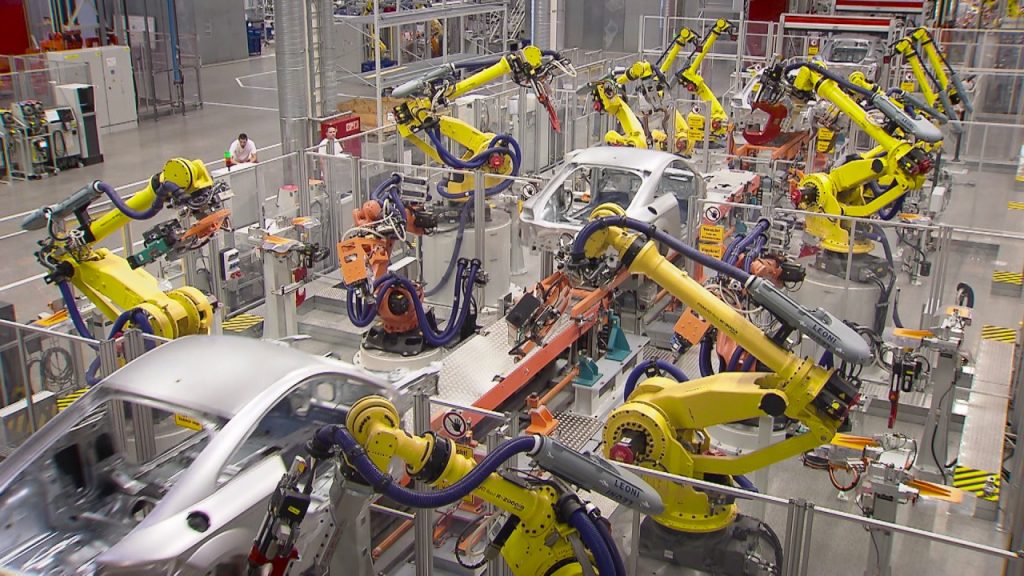
Before we dive into the specific types of industrial robots, it's important to understand their purpose and significance. Industrial robots are designed to automate repetitive tasks in various industries, increasing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. They can be found in manufacturing plants, warehouses, and assembly lines, performing tasks that were once done by humans. With advancements in technology, industrial robots have become more sophisticated, capable of performing complex tasks with precision.
Now, let's explore the different types of industrial robots:
1. SCARA Robots: SCARA stands for Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm. These robots have a horizontal arm that can move in the X and Y axes, making them ideal for tasks that require high speed and precision. SCARA robots are commonly used in assembly lines, material handling, and packaging applications.
2. Cartesian Robots: Cartesian robots, also known as gantry robots, have three linear joints that allow them to move in a straight line along the X, Y, and Z axes. These robots are often used for heavy lifting and material handling tasks in industries such as automotive and logistics.
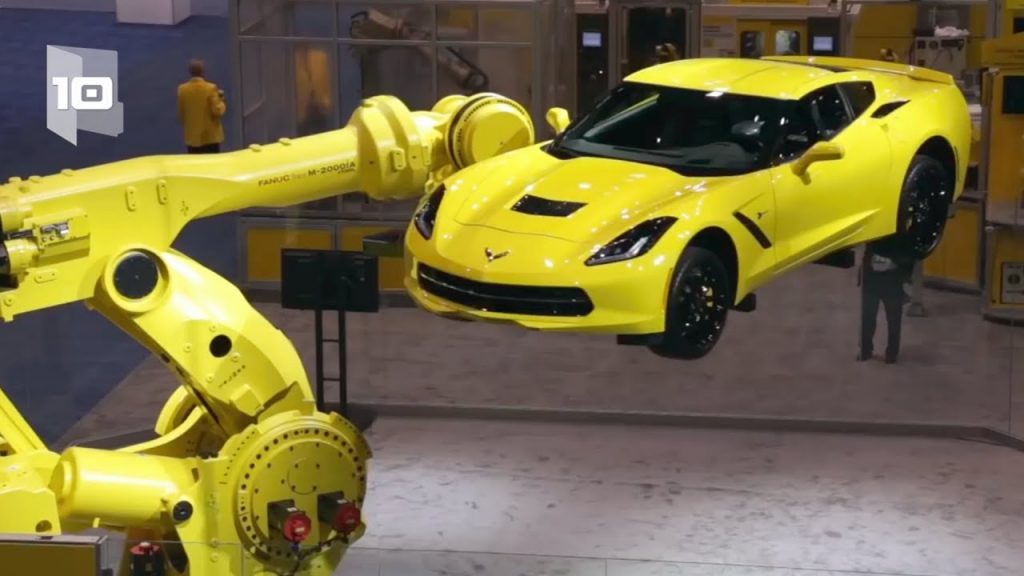
3. Articulated Robots: Articulated robots have rotary joints, similar to a human arm, which allows them to perform complex movements and reach multiple points. These robots are versatile and can be used in various applications, including welding, painting, and assembly tasks.
4. Delta Robots: Delta robots are known for their speed and precision. They consist of three arms connected to a common base, forming a triangular shape. These robots are commonly used in pick and place applications in the food and beverage industry.
5. Collaborative Robots: Collaborative robots, also known as cobots, are designed to work alongside humans in a collaborative environment. These robots have built-in safety features, such as force sensors, to ensure the safety of human workers. Cobots are used in industries where human-robot collaboration is required, such as electronics assembly and healthcare.
6. Mobile Robots: Mobile robots are equipped with wheels or tracks, allowing them to move autonomously within a defined area. These robots are often used for material transportation, inventory management, and surveillance in industries such as warehousing and logistics.
7. Autonomous Robots: Autonomous robots are capable of performing tasks without human intervention. They use sensors and artificial intelligence algorithms to navigate and make decisions. These robots are used in industries such as agriculture, mining, and exploration.
In conclusion, the world of industrial robots is vast and diverse, offering a wide range of options to suit different industries and applications. From SCARA robots for high-speed assembly tasks to autonomous robots for complex operations, each type of industrial robot has its own unique capabilities and advantages.
If you're interested in exploring the world of industrial robots further, be sure to check out the Types of Industrial Robots and Industrial Robot Arms - Chart by Reach for more information. Remember, industrial robots are revolutionizing the way we work and increasing productivity in various industries. So, why not embrace the future of automation and see how industrial robots can benefit your business?
Check the coil packing solution with a leading manufacturer for the professional solution just here: [Insert URL or contact information here] Industrial Robot
"Exploring Reach and Types of Industrial Robot Arms: A Comprehensive Chart for Efficient Automation"