Plastic Injection Molding Machine: Unveiling the Key Engineering Principles
Introduction:
In today's fast-paced world, plastic injection molding has become an integral part of manufacturing processes. It allows for the production of high-quality plastic parts with precision and efficiency. In this video, Bill delves into the key engineering principles that underlie plastic injection molding. He takes us on a journey through its history and then reveals the inner workings of a plastic injection molding machine.
History of Plastic Injection Molding:
Before we delve into the technicalities, let's take a moment to appreciate the rich history of plastic injection molding. It all started in the late 19th century when John Wesley Hyatt invented the first injection molding machine. This breakthrough innovation paved the way for mass production of plastic components, revolutionizing various industries.
Key Engineering Principles:
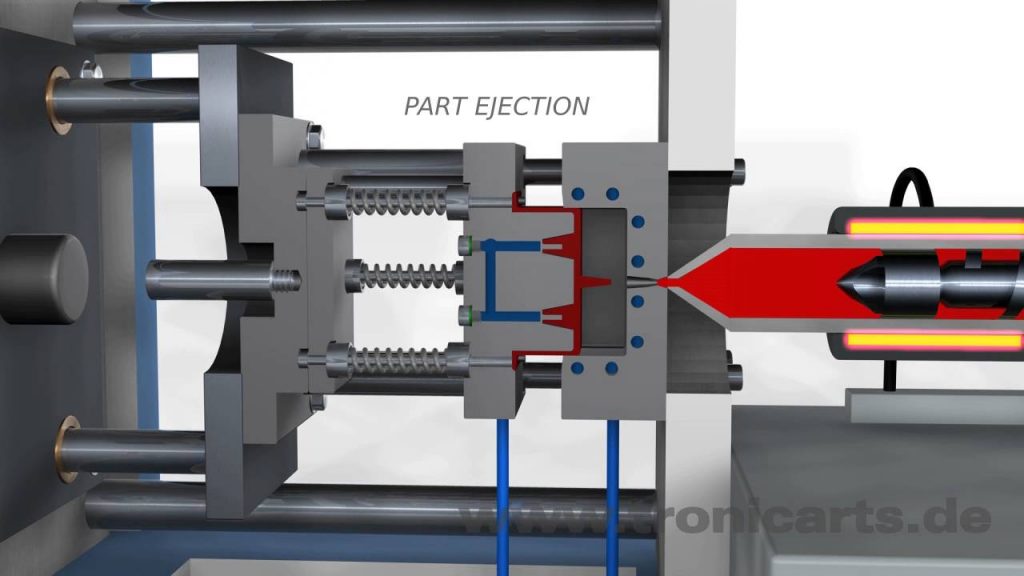
1. Mold Design and Tooling:
One of the fundamental aspects of plastic injection molding is mold design and tooling. The mold serves as a cavity where molten plastic is injected under high pressure. It is designed with intricate details to ensure precise replication of the desired part. The tooling process involves the creation of molds using different materials, such as steel or aluminum, to withstand the rigors of high-pressure injection.
2. Material Selection:
Choosing the right plastic material is crucial for successful injection molding. Various factors such as strength, flexibility, durability, and temperature resistance need to be considered. Commonly used materials include ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene, and nylon. Each material has its unique properties, making it suitable for specific applications.
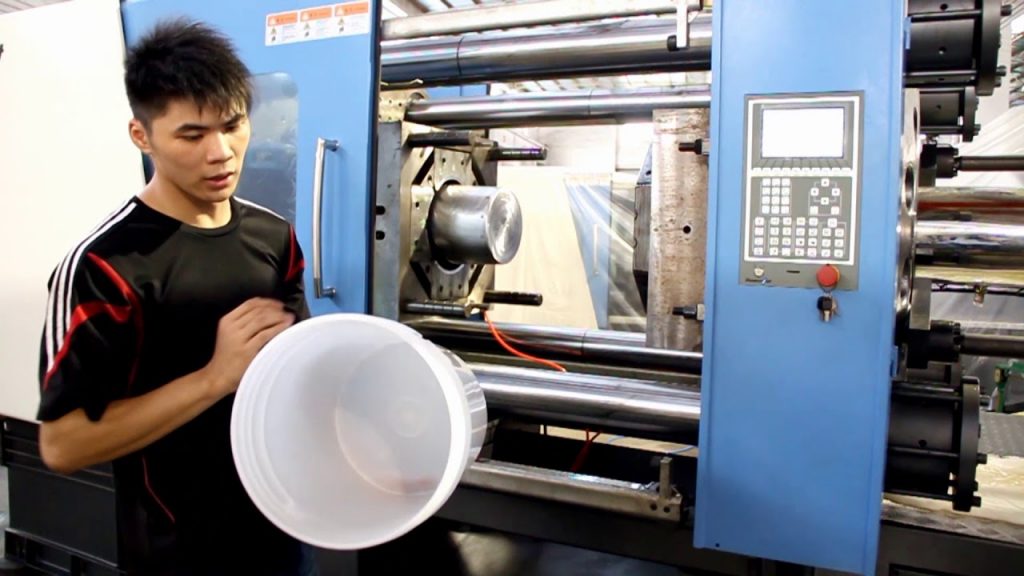
3. Injection Molding Machine:
Now, let's dive into the heart of the process – the plastic injection molding machine. This sophisticated piece of equipment consists of several essential components:
a) Hopper: The hopper stores and feeds the plastic pellets into the machine for melting.
b) Barrel and Screw: The barrel houses the screw, which plays a vital role in melting and injecting the plastic into the mold. The screw's rotation generates heat, melting the plastic pellets as it moves forward.
c) Clamping Unit: The clamping unit holds the mold in place and applies the necessary pressure during injection. It ensures that the molten plastic fills the mold cavity accurately.
d) Heating and Cooling Systems: The machine incorporates heating and cooling systems to maintain precise temperature control during the molding process. This is crucial for achieving consistent results and preventing defects.
e) Ejection System: Once the plastic has solidified within the mold, the ejection system pushes the finished part out of the mold.
Conclusion:
Plastic injection molding is a fascinating process that relies on key engineering principles. By understanding the history and inner workings of plastic injection molding machines, we gain a deeper appreciation for this technology's impact on various industries. The precision, efficiency, and versatility of plastic injection molding make it an indispensable manufacturing technique.
Check the coil packing solution with a leading manufacturer for professional solutions right here:
Note: The above article is for informational purposes only and does not endorse any specific manufacturer or company. Plastic Injection Machine
"Efficient Plastic Injection Molding Techniques: Enhancing Precision and Productivity Through Advanced Machinery"